Global Positioning System (GPS) is associated with 30+ navigation satellites circling the earth. The GPS sends signals perpetually, which helps to know where they are. In addition, there is a GPS receiver in your android and other gadgets to receive the navigations.
The GPS receiver will catch those signals and navigate you for the routes. The GPS signals calculate the distance and routes from different GPS satellites, figuring out where you are and the right path to move forward.
What is GPS?
GPS is complete with three factors: satellites, the second one is ground stations, and finally, the third one is the receiver to catch the signals to go smoothly to the right path.
The satellite is designed to figure out where we are. The ground stations work for the assurance of the exact position. The ground stations check that they are exactly where we expected.

Finally, it is the time of the receiver, which catches the signals to show the directions.
The receiver can be present in your digital gadget, which stays connected with the signals from the satellites, which helps determine how far the person is from the desired location and the best path to reach there.
How Does A GPS work?
GPS, which stands for Global Positioning System, is a technology that allows users to determine their exact location on the Earth’s surface.
This is accomplished using a network of satellites orbiting the planet, each of which transmits information about the satellite’s location and the exact time the signal was sent.
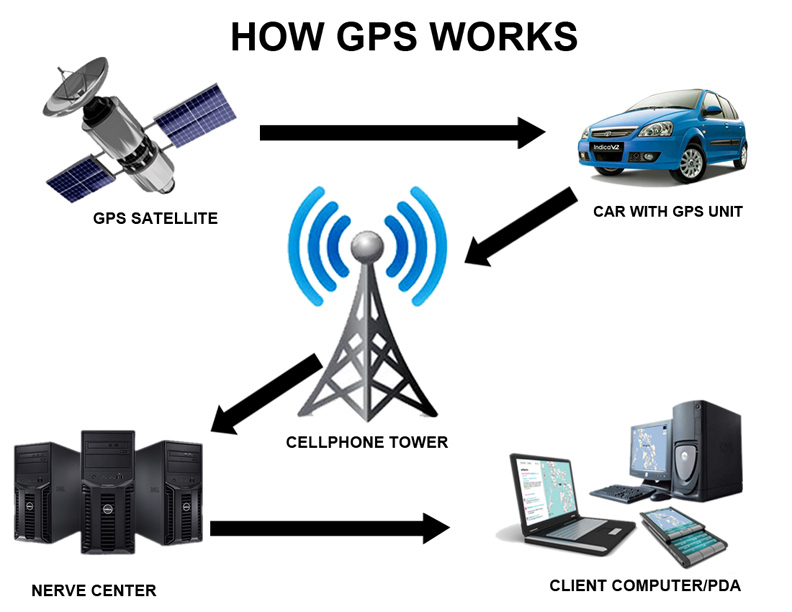
GPS receivers on the ground then receive these signals and use the information to calculate the receiver’s position on the Earth’s surface, along with other useful data such as speed and altitude.
Calculating a receiver’s position involves triangulation, measuring the distance from the receiver to multiple satellites, and using this information to determine the receiver’s location.
With GPS technology, people can navigate unfamiliar areas, track vehicles, and equipment, and find their way in the great outdoors more easily and accurately than ever before.
What Is GPS Tracking and How Does It work?
GPS tracking is a technology that allows us to track the location of any object, person, or vehicle in real time. For example, it uses a network of satellites orbiting around the Earth with a GPS receiver installed in the device to determine its position accurately.
The receiver picks up signals from at least four satellites and calculates its distance from each one. This information is then transmitted to a GPS tracking software that displays the location coordinates on a map.
GPS tracking can be used in different industries, including logistics, transportation, and personal safety. Fleet managers can use GPS tracking to monitor the movements of their vehicles, while parents can use it to track the whereabouts of their children.
GPS tracking provides a simple and effective solution to improve the safety and efficiency of various operations by providing accurate location information.
The main role of the Receiver in GPS:
The receiver calculates the distance. It finds out where you are. GPS gets confirmation of your position from four or more satellites. GPS has to be accurate with your position, so it uses four or more satellites for confirmation.

Your position is now determined from the ground station to the satellite, showing you how far you are from your mentioned location. And here, the GPS will show you the exact path to reach your destination.
Know More About GPS Navigation?
In ancient times, people looked at the sky to find ways to advance. The sailors from the ancient period used constellations to direct the path in the sea and recognize where they were.
Now navigation has become too straightforward and quick with the GPS. Now, we are just one tap away from the navigation. The Global Positioning System is the best way to find where you are and suggests the right path to reach your destination.
It doesn’t matter where you are on earth. You will receive the path suggestions anywhere and whenever you want.
In ancient times, people used the stars, and now we use satellites. The scenario is the same; we still need something in the sky to suggest directions.
What Causes GPS Inaccuracy?
Various factors, including atmospheric interference, satellite positioning, and receiver errors, can cause GPS inaccuracy. For example, atmospheric interference can occur when the GPS signal passes through ionosphere and troposphere layers before reaching the receiver.
This can cause delays in signal transmission, which may lead to errors in location accuracy. For example, satellite positioning errors can arise when GPS satellites need to be optimally positioned or are experiencing technical difficulties. This can cause inaccuracies in triangulation and location estimation.
Receiver errors also contribute to GPS inaccuracy, as the device may need to receive the signal clearly or have incorrect settings.
Additionally, natural obstructions such as tall buildings or dense tree coverage can cause GPS signals to bounce and create errors in location tracking.
Overall, GPS inaccuracy can be caused by a combination of factors that can disrupt the accuracy of location information.
Conclusion: How Does A GPS work?
In conclusion, GPS, or Global Positioning System, is a navigation system that operates with a network of satellites orbiting the Earth. GPS works by transmitting signals from satellites to GPS receivers on the ground, which then calculate the time it takes for the signal to be transmitted and received.
By combining this information from multiple satellites, a GPS receiver can pinpoint its location accurately, even in remote areas or adverse weather conditions. Additionally, GPS receivers can calculate speed, direction, and elevation based on the signals received from the satellites.
The accuracy of GPS varies depending on the number of satellites within range of the receiver, its location, and the condition of the atmosphere.
Overall, GPS is an essential tool in modern navigation and has numerous applications in various industries such as aviation, maritime, land surveying, and more.
